The Role of NAD in Cellular Health
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) plays a crucial role in numerous cellular processes necessary for survival. With growing research on aging and longevity, NAD and its precursors mainly nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) have gained significant attention for their potential benefits, including lifespan extension, metabolic health improvements, and enhanced physical performance.
However, the question remains: Can supplementing with NAD or its precursors truly enhance health and longevity? In this article, we examine the science behind these claims and evaluate whether NAD supplementation is worth considering.
Why NAD Matters
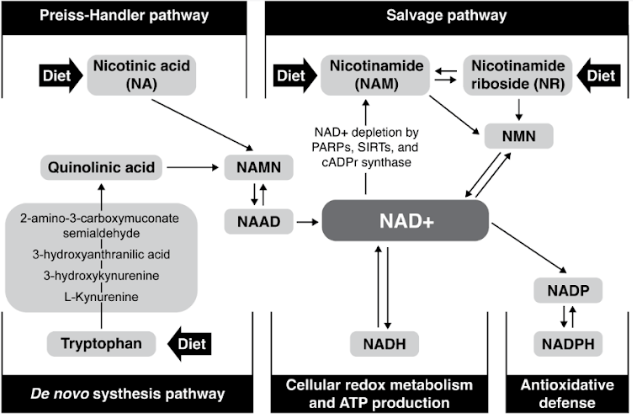
NAD is a coenzyme involved in hundreds of metabolic reactions, particularly in energy production and oxidative stress response. It exists in two primary forms NAD+ (oxidized) and NADH (reduced) which facilitate electron transfer essential for metabolism and cellular repair. Beyond its metabolic functions, NAD is also involved in DNA repair and gene expression regulation, making it a vital molecule in aging and disease prevention.

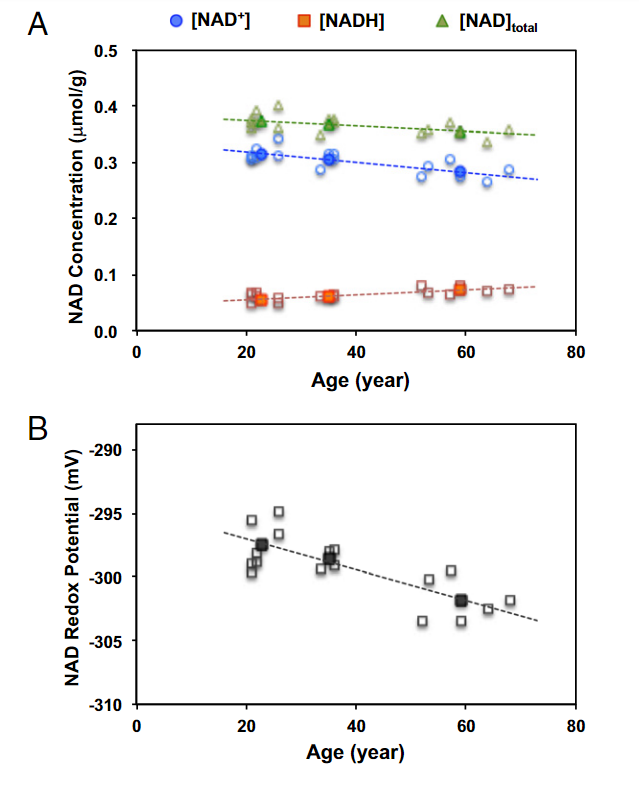
Despite its importance, NAD levels naturally decline with age, leading to potential disruptions in cellular function. This decline has spurred interest in NAD-boosting therapies as a means to counteract aging-related dysfunction.
The Rise and Fall of the Sirtuin Hypothesis
Early research linked NAD to longevity through sirtuins, a family of enzymes dependent on NAD for function. Initial studies suggested that overexpressing sirtuin genes in yeast, worms, and flies extended lifespan. However, subsequent research failed to replicate these findings in mammals, leading to skepticism about sirtuins as direct longevity regulators. Despite this, NAD remains a critical component of cellular processes beyond sirtuin activation.
NAD, Aging, and Cellular Function
Apart from sirtuins, NAD is involved in mitochondrial function, oxidative stress reduction, and DNA repair factors that influence aging and overall health. Some studies suggest that age-related NAD decline may impair DNA repair mechanisms, leading to genomic instability and accelerated aging. Additionally, mitochondrial dysfunction a hallmark of aging may be mitigated by maintaining NAD levels.
Do NAD Precursors Effectively Boost NAD Levels?
Since direct NAD supplementation has poor bioavailability, precursors like NR and NMN have been explored as alternative methods to raise intracellular NAD levels. Studies in rodents suggest that NR and NMN can increase NAD+ in tissues such as muscle and brain, though their effectiveness varies across different organs. In human trials, these precursors have shown the ability to elevate NAD levels in blood, but whether this translates to significant health benefits remains unclear.
Health Benefits of NAD Supplementation: What the Science Says
1. Lifespan Extension
For more insights on longevity research, visit Longevity Science.
The Interventions Testing Program (ITP), a rigorous lifespan study in mice, found that NR supplementation had no effect on lifespan. While NMN showed promise in one study, results were inconsistent, and further research is needed.
2. Metabolic Health
Explore additional studies on metabolic health at Metabolism Research.
Despite NAD’s role in metabolism, human trials have failed to demonstrate significant benefits for weight management, insulin sensitivity, or cholesterol levels. A 12-week study in obese men found no meaningful metabolic improvements with NR supplementation.
3. Cognitive Function and Neurodegeneration
Read more about neurodegenerative diseases at Neuroscience Today.
While rodent studies suggest NAD precursors may improve cognitive performance and reduce neuroinflammation, human trials have been mixed. Some research on Parkinson’s disease shows promise, but no strong evidence supports NAD precursors for preventing Alzheimer’s or general cognitive decline.
4. Cancer Risk
NAD’s relationship with cancer is complex. While maintaining NAD levels may support DNA repair and genomic stability, excessive NAD could fuel tumor growth in existing cancers. Some animal studies indicate that NR supplementation may accelerate cancer progression, highlighting the need for caution.
5. Cardiovascular Health
Find in-depth cardiovascular studies at Heart Health Institute.
Early research suggested that niacin (a form of vitamin B3) could lower triglycerides and improve heart health, but more recent studies show limited benefits compared to standard treatments. NR and NMN have not demonstrated significant cardiovascular improvements in clinical trials.
6. Exercise Performance
Discover more about exercise science at Performance Lab.
Given NAD’s role in energy production, researchers have explored whether supplementation can enhance physical performance. However, clinical trials show minimal effects on endurance, strength, or aerobic capacity.
Are NAD Precursors Worth Taking?
While NAD precursors show promise in certain areas, the current body of evidence does not strongly support their use for extending lifespan or dramatically improving health outcomes. Their effectiveness may depend on individual health conditions, and ongoing research will help clarify their potential.
Bottom Line
Despite the hype surrounding NAD and its precursors, scientific evidence does not yet justify their widespread use for longevity. While they may hold promise for specific conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases proven strategies like exercise, nutrition, quality sleep, and stress management remain the most reliable methods for promoting long-term health and longevity. As research continues, we will gain a clearer understanding of whether NAD precursors are truly worth the investment.

